ORIGINAL STUDIES
Aim. To evaluate possible associations between low dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) levels and cognitive impairment and their impact in cardiovascular mortality among the population 55 years and older.
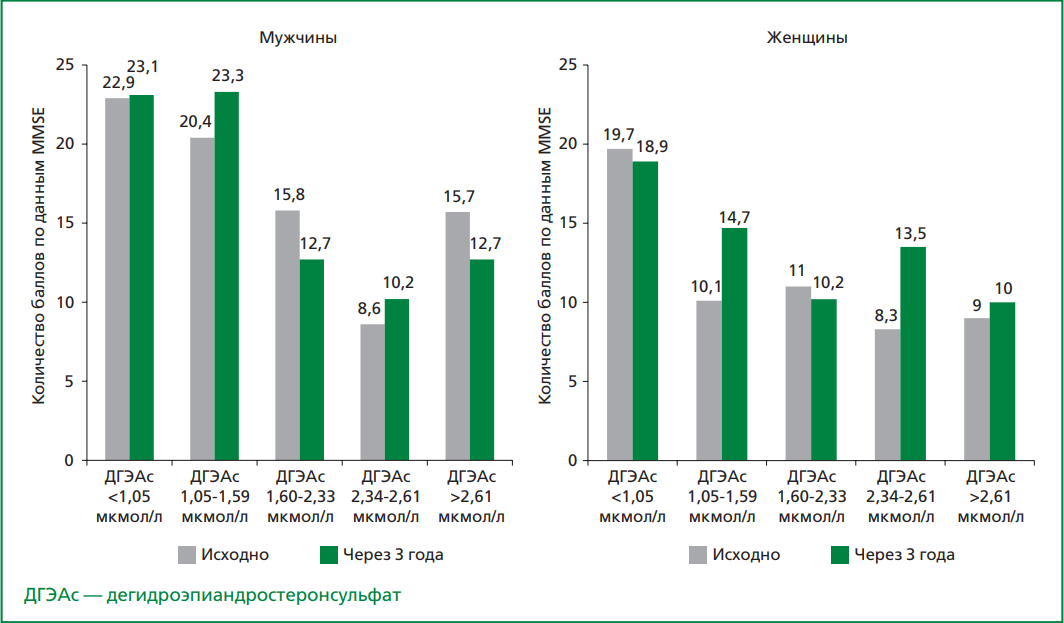
Material and methods. The present study was carried out as part of the prospective cohort survey "Stress, aging and health" in Russia. 1876 men and women aged 55 years and older were examined. Cognitive function was assessed at baseline and after 3 years using the Mini- Mental State Examination scale; a decrease in cognitive function corresponded to a sum of scores less than 24 out of 30 points. DHEAS levels were assessed in serum samples. All participants were ranked according to quintiles of DHEAS levels (>2.61 μmol, 2.34-2.61 μmol/L, 1.60-2.33 μmol/L, 1.05-1.59 μmol/L, <1.05 μmol/L). Mortality was estimated from the permanent death registry using standard methods. During the follow-up period (median 12 years), 315 deaths from CVD were registered.
Results. A total of 1876 participants aged 55 years and older (48% men and 52% women) were included in the study. The frequency of cognitive function, both baseline and after three years in men was almost independent of the DHEAS level, while in women, low levels of cognitive function were predominant in the first quintile of DHEAS. With decreasing DHEAS levels, cognitive function decreased significantly in women (1 quintile vs. 5 quintiles of DHEAS), but no such associations were found in men. In a population of men 55 years and older, both cognitive impairment (OR: 2.08; 95% CI 1.49 to 2.92) and low DHEAS levels (OR: 1.60; 95% CI 1.05 to 2.44) were significantly associated with cardiovascular mortality. Similar results were obtained in the cohort of women — the risk of cardiovascular mortality was increased in the presence of cognitive impairment by 2.3-fold (p<0.05), low DHEAS by 1.6-fold (p<0.05), respectively. The simultaneous presence of these disorders was significantly associated with CVD mortality, but only in women.
Conclusion. Based on the results of the present study, an association between baseline DHEAS levels and baseline cognitive impairment was found, but only in a female population. A prospective follow-up assessment of cognitive function failed to support the hypothesis that low DHEAS levels may predict greater decline in cognitive function. However, a significant cumulative contribution of cognitive impairment combined with low DHEAS concentration to cardiovascular mortality was observed at 12-year follow-up, but only in women.
Aim. To assess association between breast artery calcification (BAC) with ultrasound and biochemical markers of cardiovascular risk, asymptomatic and clinically expressed forms of cardiovascular diseases, as well as other chronic non-communicable diseases.
Material and methods. It is planned to include 300-400 women aged 40-74 years who underwent routine or diagnostic digital mammography at the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine and signed informed consent in a cross-sectional study. The groups will be formed on the case-control principle in a 1:1 ratio, considering age. The study protocol will include: physical examination; questionnaire to assess sociodemographic parameters, reproductive history, cardiovascular risk factors, comorbidities and drug therapy, probability of angina pectoris, intermittent claudication, history of stroke, risk of osteoporotic fractures; laboratory examination to determine parameters of lipid, carbohydrate, mineral metabolism, renal function, thyroid gland and presence of anemia; electrocardiography; duplex scanning of carotid and femoral arteries. Mammograms will be evaluated in a blinded manner by radiologists. Standard digital mammograms in craniocaudal and mediolateral projections will be analyzed. The severity of BAC will be determined using a 12-point scale.
Expected results. The data on the presence/absence of BAC and its severity will be compared with the ultrasound parameters of the atherosclerotic load of the peripheral arteries, which is a recognized marker of high cardiovascular risk, as well as traditional risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. The relationship of BAC with iron deficiency anemia, decreased bone mineral density, thyroid diseases, decreased glomerular filtration and other pathological conditions will be studied, which, according to previous studies conducted at the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine on a limited sample, can presumably be associated with the presence of BAC.
Conclusion. For Russian healthcare, the development of a methodology for assessing the probability of cardiovascular diseases as a part of a mammographic screening programs is an urgent task, but there are only a few domestic studies on the role of BAC as a marker of cardiovascular risk among women. If the hypothesis about the association between BAC and atheromatosis of the carotid and femoral arteries and other pathological conditions is confirmed, new opportunities will open up for the development and implementation of large-scale screening of cardiovascular diseases among the female population of Russia.
Aim. To assess the impact of comprehensive anticancer therapy on lipid and hormonal profile markers in individuals who underwent treatment for central nervous system (CNS) tumors during childhood.
Material and methods. A single-center, cross-sectional study included 48 patients who underwent surgical, chemotherapeutic, and radiation treatment for CNS tumors in childhood. Lipid and hormonal profiles were analyzed.
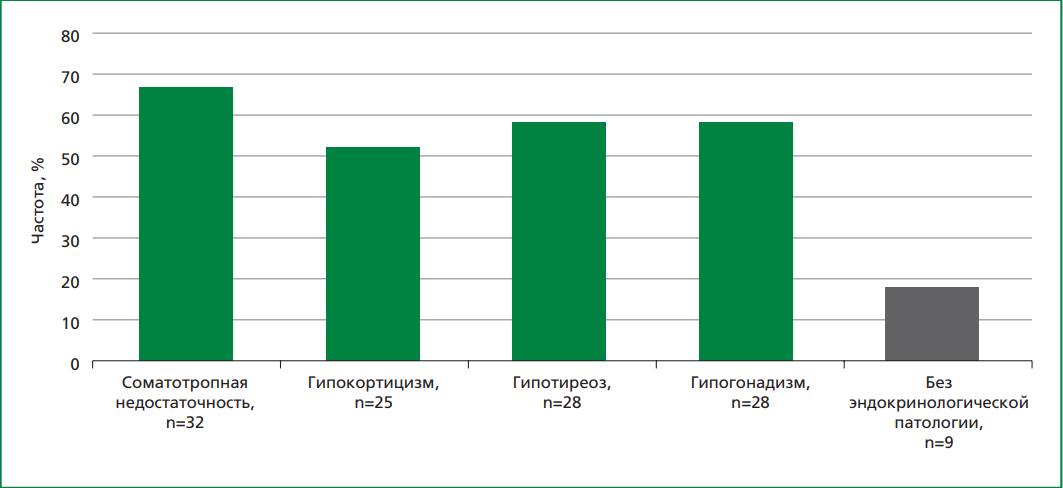
Results. In young patients (21.7±4.3 years) who had undergone comprehensive treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and cranial radiation for CNS tumors in childhood, the cumulative cranial dose of radiation therapy was found to be an independent predictor of dyslipidemia development and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels >3,0 mmol/l. Correlation analysis revealed a positive relationship between LDL-C level and the cumulative cranial dose (r=0.414; p=0.007). Statistically significant correlations were also observed between total cholesterol (TC) values and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) (r=-0.41; p=0.028), LDL-C and IGF-1 (r=-0,44; p=0,028), very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and somatotropin (r=-0.44; p=0.033). Furthermore, LDL-C level was associated with changes in thyrotropine (TSH) (r=-0.39; p=0.017), and VLDL-C was correlated with TSH (r=-0.42; p=0.016).
Conclusion. Patients who underwent complex treatment of CNS tumors in childhood demonstrated a high frequency of dyslipidemia associated with the cumulative cranial dose of radiation therapy. Considering the presence of endocrinological disorders, in particular somatotropic insufficiency and hypothyroidism, their influence on dyslipidemia development can be assumed. The potential influence of glucocorticoid therapy during oncological treatment on lipid profiles cannot be ruled out. These findings support the necessity of developing practical recommendations for dynamic follow-up of patients who have undergone comprehensive treatment for malignant CNS tumors during childhood, to ensure timely detection of cardiovascular diseases.
Aim. To explore cardiac interoception (probed by interoceptive accuracy in the mental tracking task) and its association with psychological characteristics in groups of patients with symptomatic and asymptomatic premature ventricular contractions (PVC) and controls.
Material and methods. The study included 34 patients with PVC [17 individuals formed the group with symptomatic PVC (median age: 43 years) and 17 — formed the group with asymptomatic PVCs (median age: 42 years)] and 17 healthy subjects without cardiovascular diseases (median age: 40 years) in the control group. All study participants underwent 24-hour blood pressure and Holter monitoring. Interoception was assessed by interoceptive accuracy probed by behavioral test — mental tracking task. Participants completed questionnaires to assess levels of depression, anxiety, alexithymia and body perception.
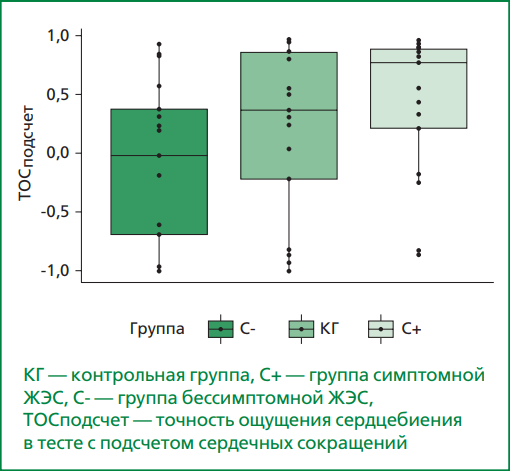
Results. Patients with symptomatic PVC had significantly higher levels of personal (p<0.001) and situational (p=0.011) anxiety compared to controls (p<0.001). The total alexithymia index was elevated in both symptomatic (p=0.004) and asymptomatic patients (p=0.028) compared to controls. Body perception (supradiaphragmatic scale of the Body Perception Questionnaire) was significantly higher in the group with symptomatic PVC compared to both the asymptomatic group (p=0.003) and the control group (p<0.001). A trend towards higher interoceptive accuracy was found in the group with symptomatic PVC (p=0.021; after correction p=0.064). No correlation was found between the level of interoception and psychological characteristics.
Conclusion. Our findings suggest a possible role of cardiac interoception in the development of PVC symptoms, which may serve as a basis for the development of non-invasive and non-pharmacological treatment methods aimed at reducing the intensity of PVC symptoms, taking into account patients’ levels of anxiety, alexithymia and body perception.
Aim. To study markers that determine residual platelet reactivity in the subacute period of myocardial infarction (MI) during the administration of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) as part of dual antiplatelet therapy.
Material and methods. 405 patients with MI (79.5% men and 20.5% women, average age 58.0 years) were divided into groups based on aggregometry results. Group 1 — 11 patients with low residual platelet reactivity, group 2 — 236 patients with optimal platelet reactivity, group 3 — 158 patients with high residual platelet reactivity (HRPR). All studies were performed on days 12-14 after MI: aggregometry on a Multiplate aggregometer (Germany) with several aggregation inducers, a blood test and a study of platelet indices, determination of endothelin-1, von Willebrand factor, sP-selectin and soluble CD40 ligand levels.
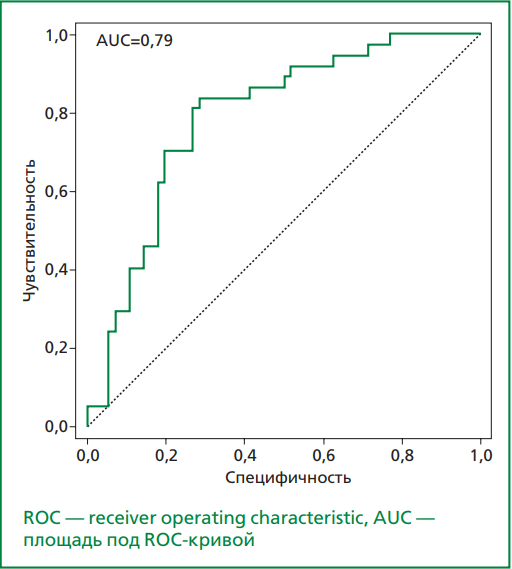
Results. Parameters influencing the ASPItest value according to univariate linear regression analysis: body mass index (β=0.53, 95% CI: 0.11-0.96; p=0.013); waist circumference (β=0.31, 95% CI: 0.14-0.49; p=0.0004); erythrocyte sedimentation rate (β=0.27, 95% CI: 0.12-0.42; p=0.0004); white blood cells count (β=1.47, 95% CI: 0.51-2.42; p=0.0027); platelets count (β=0.042, 95% CI: 0.019-0.064; p=0.00025); thrombocrit (β=36.8, 95% CI: 14.6-59.1; p=0.0012); mean platelet volume (β=1.94, 95% CI: 0.06-3.84; p=0.043); platelet distribution width (β=1.36, 95% CI: 0.22-2.51; p=0.02); creatinine (β=0.11, 95% CI: 0.011-0.21; p=0.03); C-reactive protein (β=0.18, 95% CI: 0.05-0.32; p=0.007); TRAP-test (β=0.18, 95% CI: 0.11-0.24; p=0.000001); fibrinogen (β=2.6, 95% CI: 1.17-4.02; p=0.0004). The binary logistic regression model to calculate the probability of developing HRPR to ASA included the following factors: platelet count, percentage of large platelet volume (PLCR), fibrinogen, endothelin-1 and von Willebrand factor. With a probability cutoff p₀=0.5412 for this model: sensitivity — 81.08%, specificity — 73.21%, classification accuracy — 76.34%, area under the ROC curve — 0.79 (CI: 0.696 - 0.883).
Conclusion. There are 2.7% of patients with an excessive response to ASA and 39.0% with an insufficient response to ASA on days 12-14 of MI. Clinical and biochemical markers of HRPR to ASA in the subacute period of MI are the number of platelets, PLCR, fibrinogen, endothelin-1 and von Willebrand factor.
Aim. To assess the effectiveness of clinical decision support system (CDSS) implementation strategy in increasing the frequency of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-С) monitoring in patients hospitalized for acute cardiovascular events (CVEs), in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) or dyslipidemia.
Material and methods. A non-interventional, retrospective, multicentre study assessing the impact of a CDSS with automatic electronic medical record (EMR) data processing on adherence to guidelines in patients at risk of cardiovascular diseases (SuccESS) was performed. The study included two cohorts of patients from healthcare facilities in three regions of Russia. The main cohort consisted of patients hospitalized for acute CVEs, with 12,227 patients included in the first follow-up period and 11,364 patients included in the second follow-up period. The additional cohort consisted of patients with stable CAD or dyslipidemia, with 54 469 patients included in the first follow-up period and 94,616 patients included in the second follow-up period. The study assessed follow-up findings in real-world clinical practice before and after the CDSS was implemented (first and second follow-up periods, respectively). The median duration of follow-up in the main cohort was >158 days in the first follow-up period and >227 days in the second follow-up period.
Results. In the second follow-up period the proportion of patients with available data on LDL-C control in the EMR increased from 12.3% to 18.8% (here and further — relative change: +52.3%, p<0.001) in the main cohort and from 12.3% to 19.8% (+61.7%, p<0.001) in the additional cohort. The proportion of patients with myocardial infarction and unstable angina in the main cohort who did not visit a general practitioner or cardiologist during the follow-up period decreased from 33.1% to 25.5% (-23%, p<0.001). The proportion of patients with ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack (TIA) in the main cohort who did not visit a general practitioner or neurologist during the follow-up period decreased from 66.6% to 39.3% (-41%, p<0.001). In the additional cohort, the proportion of patients who did not visit a general practitioner or cardiologist decreased from 38.2% to 27.6% (-28%, p<0.001). The use of low-intensity/moderate-intensity statin therapy decreased from 12.5% to 9% (-27%, p<0.001) in the main cohort and from 47.4% to 40% (-15%, p<0.001) in the additional cohort. However, the use of high-intensity statin therapy in the additional cohort increased from 42.7% to 49.9% (+17%). In the second follow-up period, there was a decrease in the number of hospitalizations for myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke from 3.6% to 1.7% (-53%, p<0.001) in the main cohort and from 0.1% to 0.06% (-40%, p=0.01) in the additional cohort.
Conclusion. The study findings demonstrate the positive impact of CDSS on several parameters that determine the quality and organization of medical care. The CDSS can be used to improve clinical and managerial decisions.
PAGES OF RUSSIAN NATIONAL SOCIETY OF EVIDENCE-BASED PHARMACOTHERAPY
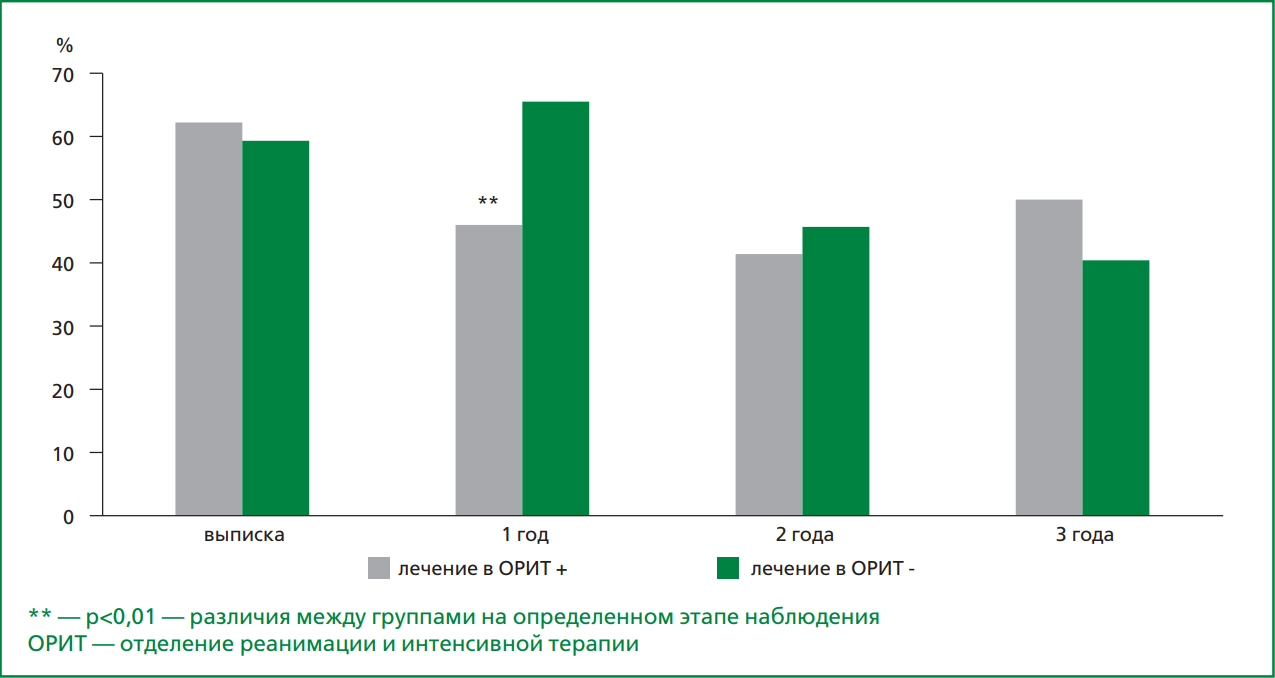
Aim. To evaluate the quality of drug treatment of patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVD) at the remote stage of follow-up after hospitalization for new coronavirus infection (COronaVIrus Disease 2019, COVID-19) within the framework of the prospective TARGET-VIP registry.
Material and methods. 1,130 people were included in the registry. The 473 (54.8%) patients with CVD were selected of the 863 patients discharged from the hospital with a diagnosis of COVID-19.
Results. The frequency of proper prescriptions of medicines upon discharge from the hospital was 60%, after 3 years this indicator decreased to 41.4% (p<0.001). During the 3-year follow-up, a clear trend was recorded in a decrease in the frequency of intake of all drugs, while for some groups of drugs this decrease reached statistically significant differences. The frequency of taking angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in patients with cerebral stroke, statins in coronary heart disease and statins in patients with cerebral stroke MI did not change significantly, although the frequency of taking these drugs at all stages of follow-up was very low and did not exceed a third of the required prescriptions. New CVD were detected in 51 patients, and the average frequency of taking proper medications for CVD was higher than in patients with already known stable CVD, 74.2% and 66.2%, respectively, p=0.047. The presence of CVD did not affect the quality of therapy in the new cases of CVD, the average frequency of taking the necessary drugs in these groups was 77.8 and 63.2%, respectively, p=0.074.
Conclusion. The quality of CVD therapy was insufficient at all stages of long-term follow-up: the frequency of proper prescriptions upon discharge from the hospital was 60%, after 3 years this indicator decreased to 41.4%. A clear trend was revealed in a decrease in the frequency of taking all drugs, while for some groups of drugs this decrease reached statistically significant differences. The quality of cardiovascular pharmacotherapy was higher with the appearance / development of new CVD in comparison with the group of stable patients with CVD, there was no significant improvement in the quality of therapy for previously observed CVD.
POINT OF VIEW
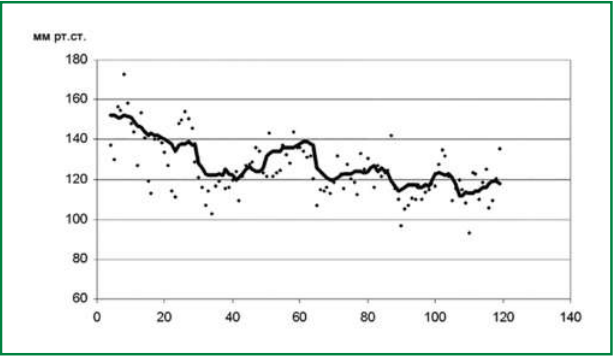
Blood pressure variability (BPV) has been studied for a long time, and recently important new information has been obtained about the prognostic value of BPV and the influence of antihypertensive therapy on it. There are three groups of VBP characteristics that are most important from a practical point of view: 24-hour BPV, BPV of average duration and visit-to-visit variability (VVV). VVV has attracted the attention of scientists in recent years. In a recent study in patients who participated in the ASCOT-BPLA cohort (mean follow-up 17.4 years) it was shown that 1) SBP VVV proved to be a strong predictor of cardiovascular complications (CVC), independent of mean BP (and possibly stronger than the latter) including in patients with well-controlled AH; 2) the CVC risk (including stroke and coronary events) remained significantly lower in the amlodipine treatment group. This finding seems particularly interesting in view of the fact that during such a long follow-up period many patients changed their treatment regimen; baseline values of office BP in both groups did not differ significantly. Thus, the independent prognostic value of VVV has received new convincing confirmation. Amlodipine may be the optimal drug for the treatment of patients with elevated BPV, but further studies are required to prove this point.
The objective is to evaluate various interventions for obesity in terms of their impact on life expectancy and the development of cardiovascular complications. When determining the degree of cardiovascular risk in patients suffering from obesity, one should rely not only on body mass index (BMI), but also on other data, namely, the presence of visceral obesity, metabolic disorders and/or cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes mellitus. The review assesses drug and non-drug treatments for obesity, as well as bariatric surgery. GLP-1 agonist drugs and bariatric surgery, despite a significant reduction in body weight, showed the least impact on life expectancy and the development of cardiovascular diseases and complications. Moreover, they are expensive to use and have side effects. Indications for bariatric surgery should be significantly limited. Bariatric surgery is most indicated for people with type 2 diabetes and/or cardiovascular diseases when they cannot be corrected with medication and non-medicinal means. Based on the available data, the Mediterranean diet, brisk walking, and metformin, despite a slower and more moderate weight loss, have the best effect on the prognosis in patients suffering from obesity. Metformin therapy should be added to the treatment of patients suffering from obesity in combination with metabolic disorders and cardiovascular diseases. In this case, one should not remain on the initial doses, but individually select doses depending on the patient’s BMI.
CLINICAL CASE
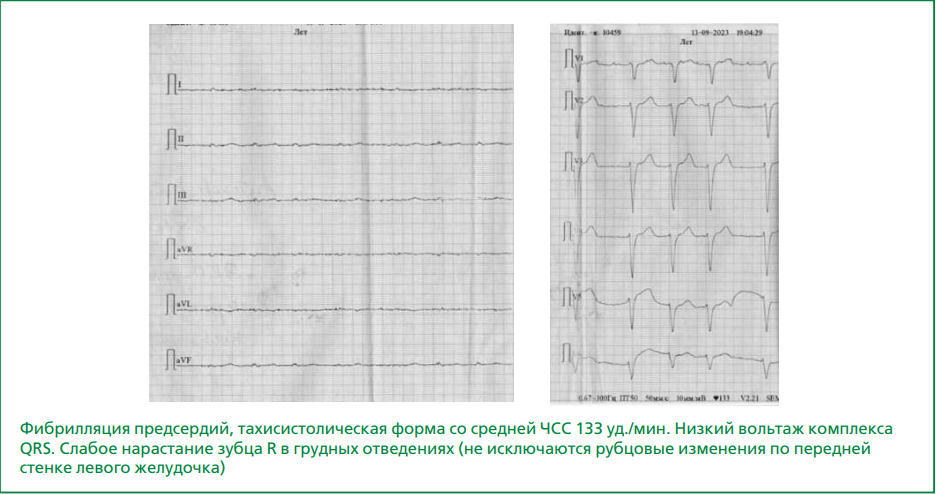
The incidence of atrial myocardial infarction (MI) varies widely, from 0.7 to 42%. This indicates that atrial MI is an overlooked rather than a rare pathology. Ischemic myocardial damage due to atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary vessels is characteristic of left atrial MI, which is often combined with left ventricular MI. In right atrial (RA) MI, the main pathogenesis link is RA overload, which occurs due to pulmonary hypertension. Isolated atrial MI is a poorly understood issue in modern cardiology; however, it may have independent clinical significance. However, there is no unified approach to pathogenesis, and there is no specific diagnostics or treatment. The article presents a clinical case of isolated RA MI (isolated necrosis of the right cardiac auricle) that developed as a result of a series of sequential events triggered by acute decompensation of chronic heart failure (CHF). The cause of this acute decompensation of CHF remains debatable. Probably, the leading contribution to CHF decompensation was made by a previous left ventricular MI with damage to the infarct-related right coronary artery basin, which causes RA involvement. Acute decompensation of CHF led to the development of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities. Pulmonary embolism developed as a result of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities and caused pulmonary hypertension, which in turn served as the basis for the development of RA MI. Due to the small thickness of the atrial wall, acute ischemic damage to the RA in this clinical case led to myomalacia and perforation of the RA wall. Due to the complexity of lifetime diagnosis of isolated atrial myocardial damage and scant clinical symptoms, this condition requires special attention and should be covered in order to develop generally accepted views on the management of patients with this pathology and to determine a list of effective treatment measures aimed at saving the patient’s life.
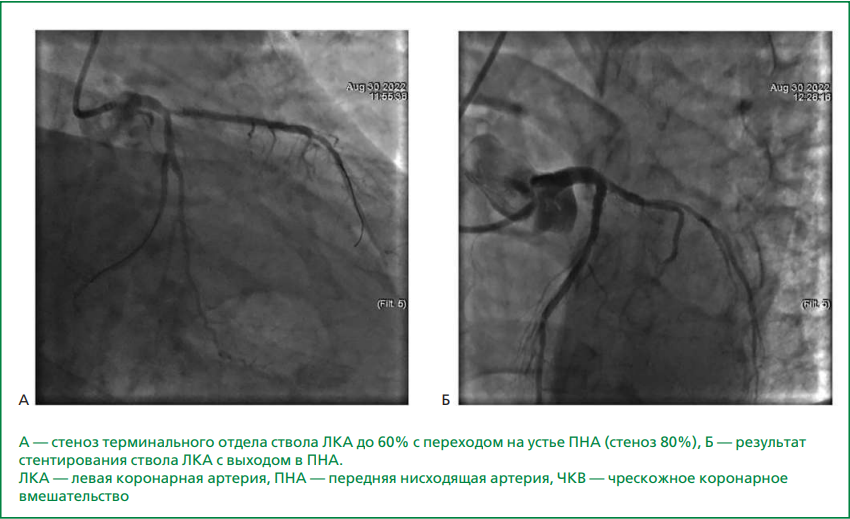
An urgent issue remains to determine the role and significance of gene polymorphism encoding components of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation system in increasing the risk of myocardial infarction and its thrombotic complications, including those associated with coronary artery stenting. This article presents a clinical case of a patient with multivessel coronary artery disease and hereditary thrombophilia — polymorphism of thrombophilia genes (heterozygote F13, ITGA2). This condition was accompanied by dramatic progression of recurrent stent thrombosis and recurrent myocardial infarction, despite ongoing triple and subsequently dual antithrombotic therapy. Repeated thrombosis necessitated surgical revascularization via coronary artery bypass surgery. Hereditary thrombophilic conditions may contribute to the multifactorial nature of stent thrombosis development, complicating both the diagnosis of its causes and the choice of antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapy options, especially given the limited time frame in cases of acute stent thrombosis. Risk factors for stent thrombosis in this clinical case include hereditary thrombophilia, multivessel coronary artery disease involving the left main coronary artery, multiple stent implantation, myocardial infarction, and repeated revascularization. A number of gene mutations associated with an increased risk of thrombosis were identified, which may have varying clinical significance. However, from the perspective of genetic polymorphism, it is not possible to completely rule out their influence. Regarding the choice of antithrombotic therapy in patients with congenital thrombophilia, recurrent or treatment-resistant thromboses of unknown etiology, rare blood clots localization, randomized clinical trials on the efficacy of direct oral anticoagulants remain insufficient. Therefore, warfarin remains the treatment of choice for this specific group group of patients. Diagnosis of hereditary thrombophilic conditions influences the choice of rational therapy and secondary prevention of thrombotic complications.
ISSN 2225-3653 (Online)