ORIGINAL STUDIES
Aim. To evaluate and compare the diagnostic performance of the 2019 European Society of Cardiology pre-test probability (PTP) model and the coronary artery disease (CAD) consortium basic and clinical models in predicting obstructive CAD in patients with stable angina.
Material and methods. This cross-sectional study included 366 patients (mean age 64.8 years, 62.6% male) with suspected stable angina who underwent coronary computed tomography angiography. Obstructive CAD was defined as the presence of ≥50% stenosis in epicardial coronary artery segments with a diameter of ≥2.5 mm. We assessed clinical characteristics and cardiovascular risk factors. The PTP values from the three models were calculated, and their diagnostic performance was evaluated using area under the receiver operating characteristic curves and the Hosmer-Lemeshow test for calibration. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values were also analyzed.
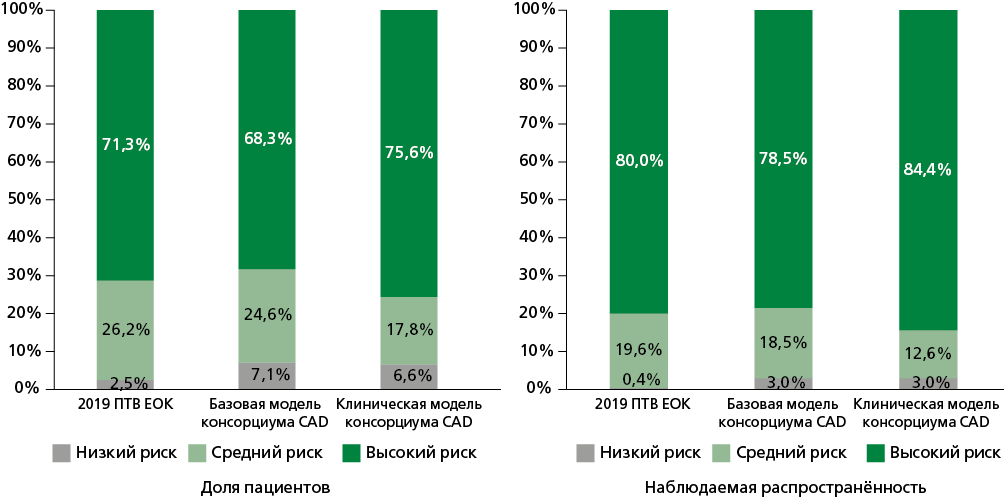
Results. Obstructive CAD was detected in 270 (73.8%) patients. Patients with obstructive CAD had higher rates of male sex, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, and typical and atypical angina (all p<0.05). The CAD consortium clinical model provided the most accurate estimate of obstructive CAD prevalence in high-risk patients (76.6% expected vs 84.4% observed), while the 2019 ESC PTP model was more accurate in low-risk patients (2.5% expected vs 0.4% observed). The CAD consortium clinical model demonstrated the best diagnostic performance with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.760 and good calibration (Hosmer-Lemeshow test, p=0.823). This was followed by the CAD consortium basic model (AUC=0.755), and the 2019 ESC PTP model, which had the lowest performance (AUC=0.701, poor calibration, p=0.001). The CAD consortium clinical model, with a cut-of value >33%, had a sensitivity of 66.7%, specificity of 79.2%, a positive predictive value of 90%, and a negative predictive value of 45.8% in predicting obstructive CAD.
Conclusion. The CAD consortium clinical model showed superior accuracy in predicting obstructive CAD in stable angina patients, especially in high-risk groups, compared to the 2019 ESC PTP and CAD consortium basic models. Its strong diagnostic performance and reliable calibration make it a better tool for CAD risk assessment.
Aim. To analyze the individual association of arterial hypertension (AH) prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control with regional characteristics within the national epidemiological ESSE-RF study (2012-2022), assessing the impact of the COronaVIrus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
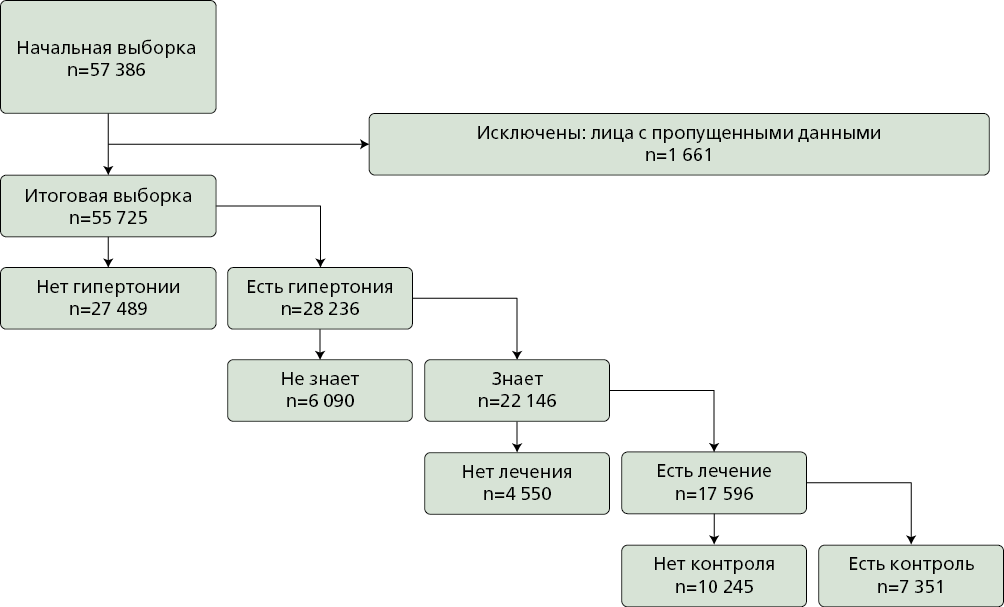
Material and methods. The analysis used pooled data from the ESSE-RF study across three time periods: ESSE-RF-1 (2012-2014), ESSE-RF-2 (2017-2018), ESSERF-3 (2020-2022). The final analytical sample across all three periods 55.725 men and women aged 25-74 years. The presence, awareness, treatment and of AH were considered as individual outcomes. Regional living conditions were assessed using the "Economic", "Demographic", "Industrial" and "Social" indices based on data from the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine. Statistical analysis was performed using generalized estimating equations (logistic regression models) with calculation of Odds Ratios and 95% Confidence Intervals. To assess the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the associations between regional living conditions and AH prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control, separate analyses were performed in the ESSE-RF-1 2012-2014 and ESSERF-3 2020-2022 samples.
Results. Improvement of social living conditions was associated with a decreased probability of AH (0.90; 0.85-0.95), increased AH treatment (1.13; 1.02-1.25), and control (1.11; 1.01-1.22). A demographic shift toward a younger age structure in regions was associated with a decreased AH probability (0.83; 0.76-0.91). Increasing industrial development in regions was associated with decreased AH treatment (0.87; 0.80-0.96). Compared to sex, age, and obesity, regional indices contributed significantly less to the studied outcomes. Nevertheless, the contribution of regional living conditions was comparable to such individual predictors as education level, income, and urban/rural residence. Substantial differences were observed in the associations between regional indices and AH treatment/control in the pre-pandemic (presence of multiple associations) and pandemic (associations virtually absent) study periods.
Conclusion. The results of the study indicate associations of AH prevalence, treatment, and control with regional living conditions. The attenuation or even inversion of associations between regional characteristics and AH treatment/control during the COVID-19 period confirms the significance of the pandemic as a powerful driver of changes in individual and population health-related behavior.
Aim. To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of cavutilide in patients with a history of unsuccessful cardioversion to terminate current persistent and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) episode.
Material and methods. The retrospective study included 55 patients (mean age 60±8 years; male/female ratio 37/18) with paroxysmal (n=15) and persistent (n=40), who had unsuccessfully attempted to terminate the current episode of arrhythmia using electrocardiography. All patients received сavutilide in the intensive care unit according to the following regimen: 5 μg/kg-5 μg/kg-10 μg/kg-10 μg/kg. After each bolus and before the next one, ECG parameters (rhythm, QT interval) and the patients’ general condition were assessed; the interval between administrations was 15 minutes. Administration was halted if sinus rhythm (SR) was restored, heart rate (HR) fell below 50 bpm, QTc exceeded 500 ms, or arrhythmogenic effects occurred. Patients were monitored telemetrically for 24 hours to assess efficacy and safety.
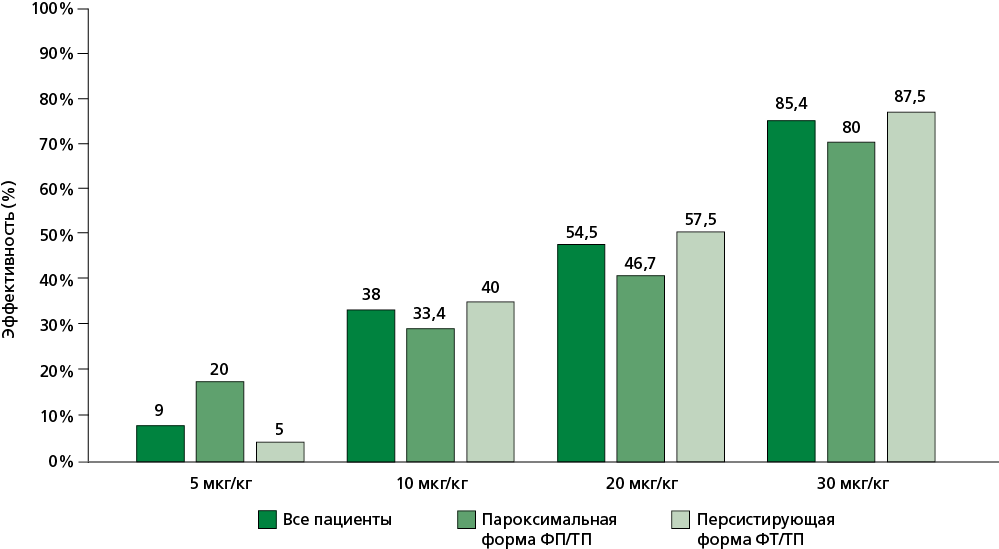
Results. SR was restored in 47 (85.4%) out of 55 patients, with a median restoration time of 40 [15-240] minutes. Five patients (9%) achieved SR after the initial of 5 μg/kg dose. Sixteen additional patients responded to 10 μg/kg (cumulative efficacy: 38%). Nine further patients achieved SR at 20 μg/kg (cumulative efficacy: 54.5%). The remaining patients required the maximum 30 μg/kg dose. QTc prolongation >500 ms occurred in 12 (21.8%) patients, though none developed sustained ventricular arrhythmias. Transient HR reduction <50 bpm occurred in 4/55 patients (7.2%) during arrhythmia termination.
Conclusion. Cavutilide demonstrates high effectiveness and safety in restoring heart rhythm in patients with prior unsuccessful electrical cardioversion attempts. These findings support considering pharmacological cardioversion with cavutilide in such cases.
Aim. To study the effect of different intensities of statin therapy on androgen status and erectile function in men aged 40-65 years with high and very high cardiovascular risk. Additionally, to assess the association between sex hormone levels, erectile function parameters, and traditional cardiovascular risk factors, arterial stiffness, and endothelial function in this patient category.
Material and methods. It is planned to conduct a prospective randomized controlled trial, including 150 male patients aged 40-65 years, undergoing routine preventive examinations in the clinic of Moscow State University, having a high and very high risk of CVD and meeting the inclusion criteria. Group 1 (n=75) will receive pitavastatin at a starting dose of 1 mg/day. Group 2 (n=75) will receive rosuvastatin 20 mg/day. After 3 months, the biochemical parameters will be monitored, and dose titration of pitavastatin to 2-4 mg/day and/or rosuvastatin to 40 mg/day will be performed if necessary. Patient recruitment to the study will occur over 9 months at a single research center. Patients will be monitored with an objective assessment of erectile function parameters, blood analysis (including androgen status), central arteries stiffness, and endothelial function for 6 months from the moment of activation. Follow-up visits are scheduled at 1, 3 and 6 months.
Results. The expected result of testing the research hypothesis is that statin therapy will not have a negative effect on androgen status and erectile function in men. Intensive statin therapy will have a greater positive effect on endothelial function, which may lead to an improvement in men’s erectile function.
Conclusion. The study was planned under the assumption that statin therapy would not have a negative effect on androgen status and erectile function in men aged 40-65 years. It is also suggested that the positive effect of statins on endothelial function and vascular stiffness may lead to an improvement in erectile function among men with high and very high cardiovascular risk. If the hypothesis is confirmed, the results obtained will help improve statin treatment adherence in male patients and, as a result, increase the effectiveness of prevention of cardiovascular events.
Aim. To study the relationship between plasma levels of lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), and the occurrence of stent restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), as well as the achievement of target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level with lipid-lowering therapy.
Material and methods. The prospective study included 92 patients (mean age 64.0 years, 79.5% male, 20.5% female) diagnosed with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who underwent stenting of a clinically significant or infarction-related coronary artery. At the same time, blood flow in the remaining coronary arteries was visually assessed during selective coronary angiography (SCA). In cases of hemodynamically significant stenosis of a coronary artery not associated with ACS, ranging from 70% to 90%, the patient was invited to consult a cardiologist in a month to decide on myocardial revascularization through stress testing, taking into account the patient’s clinical status (complaints). If necessary, repeat SCA for therapeutic purposes was performed after 1-2 months to visualize neointima formation and the degree of restenosis within the stent previously implanted in the infarct-related artery, in combination with the determination of Lp(a), VEGF, and TGF-β in blood plasma. The achievement of the target LDL-C level against the background of lipid-lowering therapy was assessed. Patients were divided into 2 groups: with detected restenosis or neointima (n=49) and without restenosis (n=43). The clinical, laboratory, and angiographic data obtained in the groups were compared.
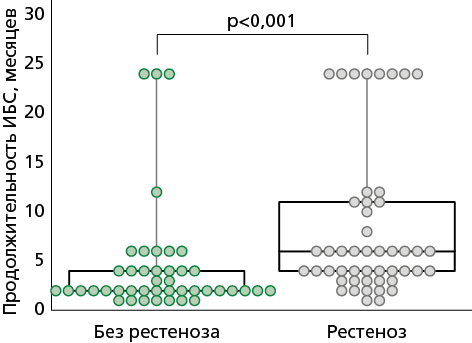
Results. The development of restenosis is associated with a prolonged course of CAD — 6.0 (4.0; 11.0) months (p<0.001), stable CAD was recorded in 42.86% (p=0.01), chronic kidney disease (CKD) 3A 32.65% (p=0.02) and the use of bare-metal stent (BMS) was 79.59% (n=39) (p<0.001), Lp(a) level >30 mg/dL 36.73% (p=0.01). Analysis of combinations revealed that having both TGF-β and Lp(a) within normal ranges simultaneously was a protective factor against restenosis development (odds ratio=0.2 [95% confidential interval: 0.07-0.56]), as was having both Lp(a) and VEGF within normal ranges (odds ratio=0.33 [95% confidential interval: 0.14-0.82]).
Conclusion. In CAD patients 1-2 months post-PCI for ACS, restenosis development is associated with longer CAD duration, CKD stage 3A, use of BMS, and elevated Lp(a) levels >30 mg/dL, irrespective of achieving the target LDL-C level <1.4 mmol/L. Elevated baseline Lp(a) values combined with VEGF and TGF-β levels in blood plasma indicates a high risk of stent restenosis, which may be new biomarkers for predicting the progression of coronary artery disease. These results confirm the need to develop practical guidelines for the dynamic monitoring of this patient group.
PAGES OF RUSSIAN NATIONAL SOCIETY OF EVIDENCE-BASED PHARMACOTHERAPY
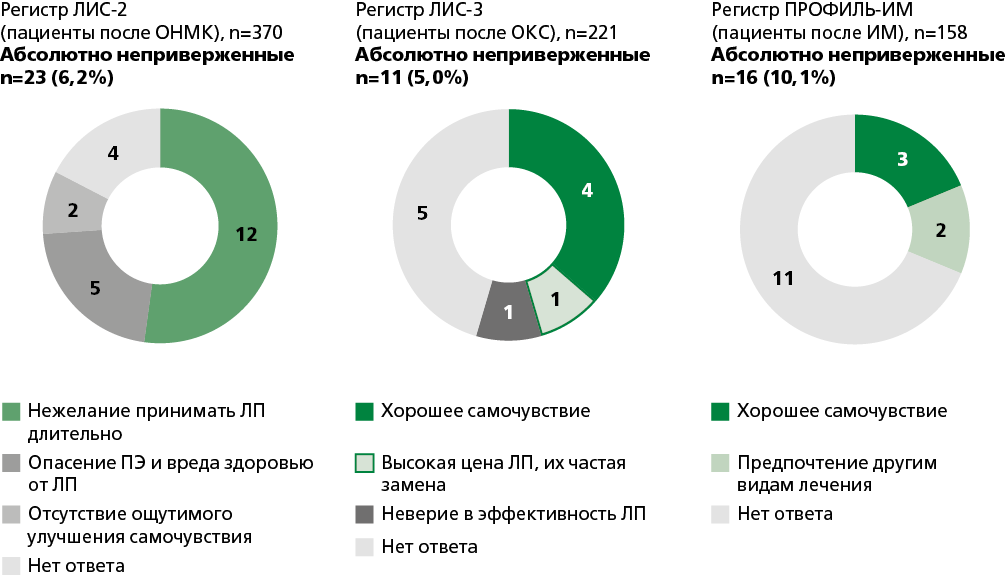
This article addresses the issue of refusal of pharmacological treatment. Limited literature data concerning the clinical significance of treatment refusal in patients with internal organ diseases are presented. Original foreign studies focusing on treatment refusal in patients with chronic non-communicable diseases, particularly those with cardiovascular conditions, are rare. Most of these studies examine not only the refusal to take medications but also the discontinuation of specific therapeutic procedures, as well as the underlying reasons for such refusals. An analysis was conducted of Russian prospective clinical registries for cardiovascular diseases, which have recorded instances of complete cessation of pharmacological therapy or the phenomenon of absolute non-adherence. The frequency of complete discontinuation of treatment ranged from 1% to 10.1%. The main reasons for the complete discontinuation of medication included satisfactory health status, reluctance to engage in prolonged medication use, and high costs associated with treatment. It is demonstrated that complete discontinuation of therapy may have a negative impact on disease outcomes. Thus, a certain proportion of patients with cardiovascular diseases completely refuse treatment, despite being provided with recommendations. This can be partly attributed to the patients’ relatively good well-being. Additionally, poor awareness regarding the efficacy of prescribed medications seemingly plays a significant role. Therefore, a promising approach to prevent the phenomenon of absolute non-adherence among patients with chronic non-communicable diseases is regular monitoring and educating them about the fact that the prescribed therapy can not only alleviate disease symptoms but also improve the prognosis and reduce the risk of complications.
CURRENT QUESTIONS OF CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
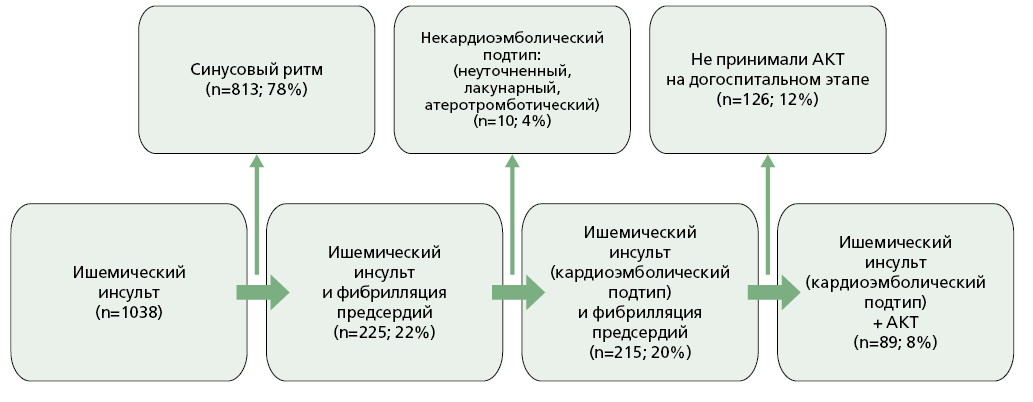
Aim. To evaluate the characteristics of anticoagulant therapy (ACT) use in patients with cardioembolic (CE) subtype ischemic stroke (IS) and atrial fibrillation (AF) hospitalized in a specialized vascular center.
Material and methods. A cross-sectional study was conducted at the Vascular Center of Botkin City Clinical Hospital from April 2022 to April 2023. Adults (≥18 years) with confirmed CE-subtype IS and documented AF, presenting within 12 hours of symptom onset and receiving anticoagulants for over one month prior to admission, were eligible. Patients with hemorrhagic stroke or non-CE IS subtypes, those lacking data on anticoagulant use, or those who declined to participate were excluded.
Results. Among 1.038 patients with IS, 215 (20.7%) were diagnosed with the CE subtype in the setting of AF. More than half (n=109) were not receiving ACT at the time of stroke onset. A total of 106 patients who had been on outpatient ACT were included; rivaroxaban (n=56), apixaban (n=30), dabigatran etexilate (n=11), and warfarin (n=9). The mean patient age was 77.8 years, with an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 6. In 33.9% of patients, the prescribed doses of direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) did not correspond to clinical guidelines (e.g., unjustified dose reductions of rivaroxaban and apixaban were identified). The median National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score at admission was 7, and in-hospital mortality reached 30.2%. Elevated mortality was associated with severe stroke presentation (NIHSS score > 8 in half of the patients) and a high burden of comorbidities: hypertension in 95.2%, chronic heart failure in 60.4%, type 2 diabetes mellitus in 30.1%, and prior myocardial infarction in 37.7% of patients.
Conclusion. The high incidence of IS despite ongoing anticoagulation highlights the need for routine monitoring of DOAC plasma levels, regular assessment of treatment adherence, and systematic education of patients and their families regarding the importance of strict adherence to prescribed anticoagulant regimens.
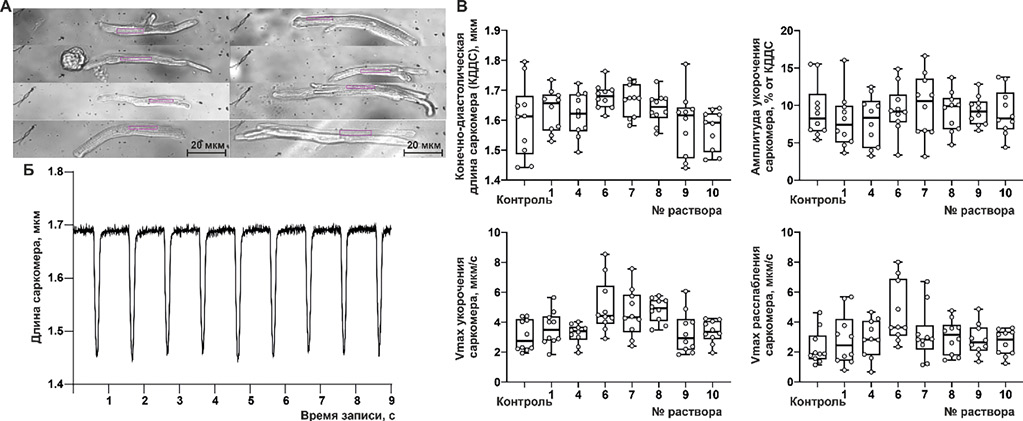
Aim. To identify the most promising drug composition for replenishing intracellular magnesium deficiency by eveluating the physicochemical properties of magnesium complex compounds and conducting experiments on isolated rat atrial cardiomyocytes.
Materials and methods. The study assessed the osmolality of solutions containing magnesium complex compounds, their extraction into organic solvents of different polarity (chloroform and butanol), and diffusion through a cell membrane model (lecithin-modified paper filter). In experiments on isolated rat atrial cardiomyocytes, the compositions were tested for replenishment of intracellular (cytosolic) magnesium deficiency using laser scanning (confocal) microscopy.
Results. Based on physicochemical testing of magnesium preparations and experiments conducted on cardiomyocytes of laboratory animals, the most promising system for replenishing intracellular magnesium was a system based on magnesium aspartate, in which the ratio of magnesium ions to aspartic acid is 1 to 2.5. Thirty-minute incubation with this preparation led to increased cytosolic [Mg2+]i by 115% compared to control. Removal of excess potassium ions from the potassium aspartate and magnesium system shifted pH toward a more physiological range (from 6.8 to 7.3), while the lipophilic properties (organic solvent extraction and lecithin filter diffusion) doubled.
Conclusion. The paper presents a methodological approach for analyzing of magnesium complex compounds for replenishing its intracellular deficiency, emphasizing complex type, concentration, lipophilicity, and original system osmolality. Experimental findings were confirmed in a translational experiment with isolated atrial cardiomyocytes, which allows us to identify the most promising complex in relation to replenishing intracellular magnesium deficiency.
CLINICAL CASE
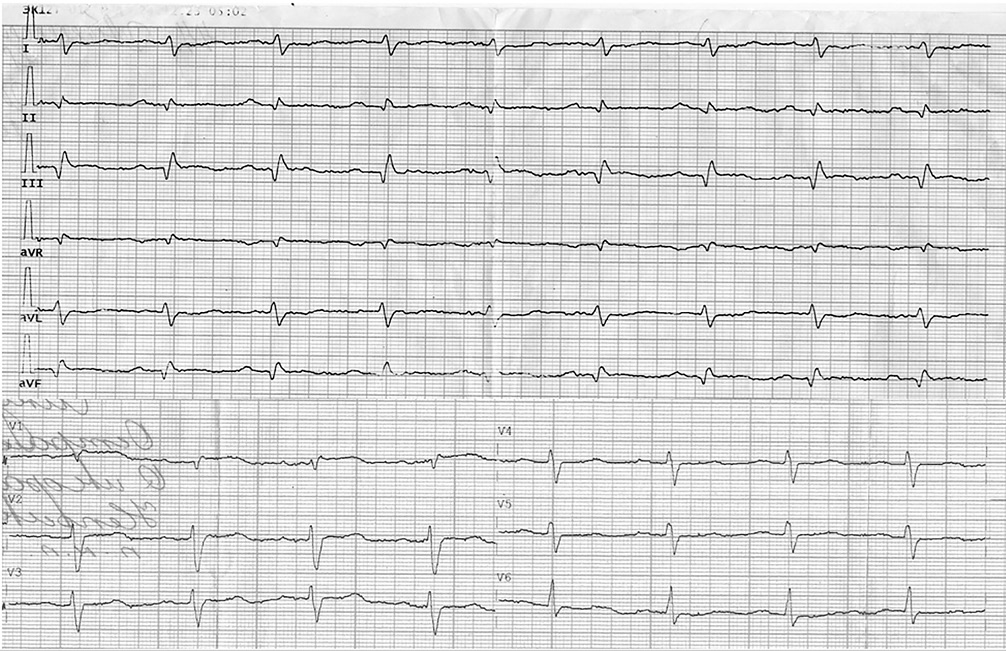
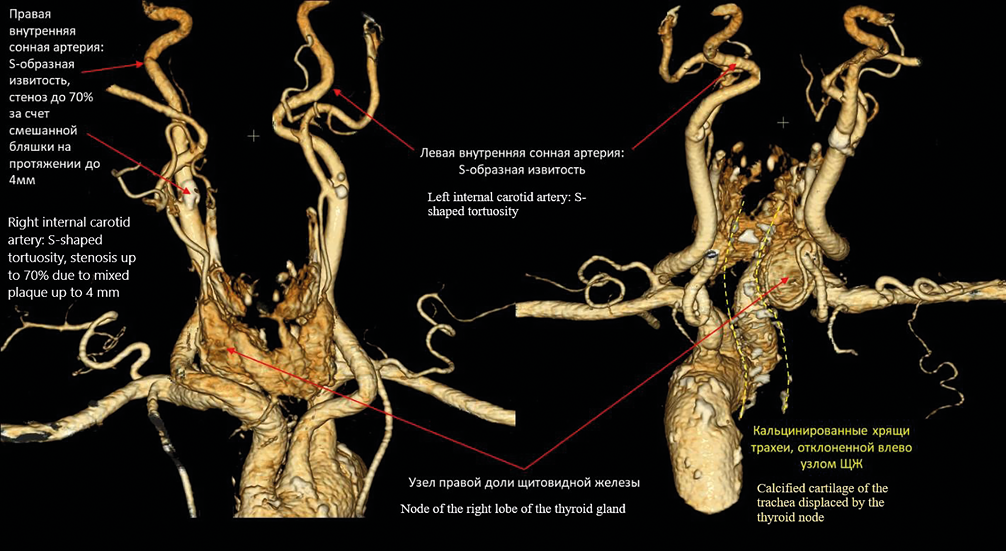
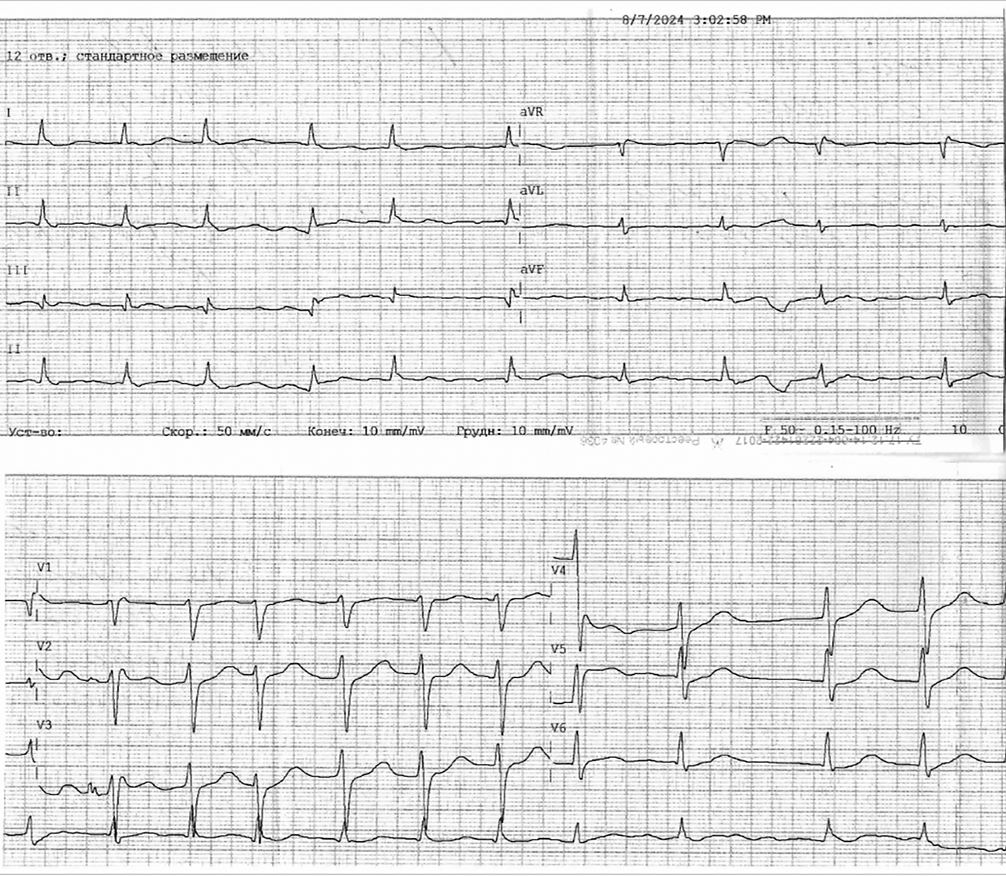
The article describes a clinical case of a 44-year-old woman with almost simultaneous onset of massive pulmonary embolism (bilateral involvement) secondary to posterior tibial vein thrombosis with a floating thrombus, and embolic myocardial infarction caused by paradoxical embolism through an atrial septal defect. These events occurred against a background of severe anemia of unknown etiology. The management strategy initial primary percutaneous coronary intervention for type 2 myocardial infarction and thrombotic occlusion of the posterior interventricular artery with stent implantation, and subsequent thrombolytic therapy for pulmonary embolism. The article further discusses the complex issues of prescribing and adjusting antithrombotic therapy based on decisions by medical council, which led to significant clinical improvement by the time of the patient’s discharge.
The mechanisms of drug-induced myopathies include direct myotoxicity, immune-mediated and indirect muscle damage. Clinical manifestations range from asymptomatic or minor myalgia and muscle weakness to chronic myopathy with severe weakness and, in rare cases, rhabdomyolysis with release of cellular breakdown products into the bloodstream and intercellular space. Although muscle symptoms are the most common adverse events when using statins, they do not pose a real threat in most cases. Rhabdomyolysis is an extremely rare complication of statin therapy. The case illustrates the difficulties that arose in the differential diagnosis of rhabdomyolysis etiology in a patient receiving high-dose statin therapy. The widespread use of high-intensity statin therapy, often accompanied by the simultaneous use of ticagrelor and proton pump inhibitors, requires caution regarding treatment safety, particularly in elderly patients.
Given the high prevalence of allergic and cardiovascular diseases, clinicians must remain vigilant to the possibility of Kounis syndrome (KS), which involves the cooccurrence of an allergic reaction and acute myocardial infarction (AMI). The article describes a case of KS in a 62-year-old patient, without atherosclerotic coronary artery disease, during the infusion of a plasma-substitute, dextran, used by the patient for self-medication and resulting anaphylactic shock. The diagnosis of AMI was confirmed by elevated myocardial necrosis biomarkers, as well as electrocardiographic and echocardiographic changes. Patient management adhered to current clinical guidelines for AMI and allergic reactions. The distinctive feature of this clinical case is the development of type I KS triggered by dextran, and the multifactorial etiology of AMI. This case demonstrates the importance of recognising KS, advocates for restricting self-treatment practices, and highlights the need for preventive counselling regarding its potential consequences.
POINT OF VIEW
The article examines the evolution of risk assessment strategies for thromboembolic complications in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), with a focus on the role of gender in the CHA2DS2-VASc score, which has long been the standard for stroke risk stratification. The analysis of historical approaches of various feasibility study risk assessment strategies, starting from the recommendations of 2001, when there was no single risk assessment, to the current international guidelines of 2024, led to the conclusion that special attention should be paid to the expediency of including female sex as an independent stroke risk. Current data indicate that gender identity has been leveling off over time in the incidence of strokes among patients with AF and suggest considering the female sex only as an age-dependent modifier of stroke risk. The results of studies from different countries (Finland, Denmark, Great Britain) confirm a decrease in the influence of the female sex as an independent stroke risk factor, discussing the expediency of switching to a simplified CHA2DS2-VA score (excluding gender). The authors emphasize the importance of individualized episodic re-evaluation of thromboembolic complications risk, particularly in patients with comorbidities, and also emphasize the need for caution when implementing changes in domestic practice, considering the unique characteristics of Russian healthcare and its disparities with systems in other countries.
ANNIVERSARY
ISSN 2225-3653 (Online)